Issue 130: Poverty in Georgia (2010-2020)
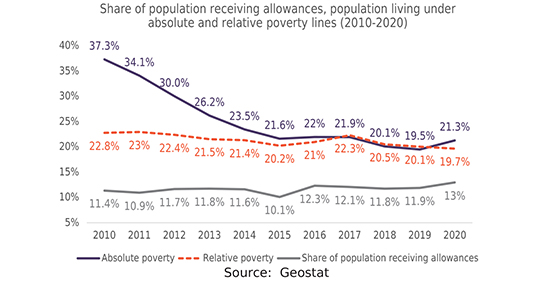

Poverty alleviation remains one of the biggest challenges for the world, including Georgia. Methods applied to determine the poverty rate vary from country to country, so in order to gain a broad understanding of the current situation regarding poverty in Georgia at the international level, it is important to take into account a variety of indicators.
In 2020, GDP per capita in Georgia amounted to 4279 USD, ranking it 122nd in the world and 3rd among Eastern Partnership (EaP) countries. Meanwhile, the Human Capital Index (HCI) calculates the contributions of health and education to worker productivity with Georgia scoring 0.57 in 2020, ranking 85th out of 174 countries world and having the lowest score among EaP countries.
Multidimensional poverty encompasses various forms of deprivation experienced by poor people such as poor health, lack of education, inadequate living standards, poor quality of work and the threat of violence. In 2019, 3.8% of the population in Georgia was multidimensionally poor, ranking 57th out of 120 countries in the world and first among EaP countries. The Gini Index measures income distribution within a society. In 2021, Georgia scored 36.4 on the Gini Index, ranking 76th out of 165 countries and having the highest inequality rate among EaP countries. In terms of life expectancy, in 2020 average life expectancy in Georgia was 74.2 years, ranking it 101st in the world and 3rd among EaP countries. Taking into account these indicators, Georgia, on an international level, is an upper-middle-income country with moderate rates of inequality and life expectancy. Due to its poor educational and healthcare systems, Georgia has been unable to mobilize its human capital to achieve a higher level of economic development.